Open5gs and OAI-GNB
5G end to end (SA) communication demo using hardware equipment with Open5gs and OpenAirInterface gNB.
This setup uses 2 helm charts generated by Gradiant: open5gs and oai-gnb. These charts are packaged and available at Gradiant’s DockerHub repo: https://hub.docker.com/u/gradiant
If you want to have the repo in local you can pull it:
helm pull oci://registry-1.docker.io/gradiant/open5gs --version 2.2.0
helm pull oci://registry-1.docker.io/gradiant/oai-gnb --version 0.3.1
Equipment requirements
The following hardware equipment is required in order to replicate the setup used for this tutorial:
- USRP Software Defined Radio Device, which is supported by the UHD (USRP Hardware Driver) Software. In our setup, an Ettus USRP B210 was used.
- UE (User Equipment) suitable for connecting to this network deployment. In our setup, a tablet (Samsung Galaxy Tab S7+ 5G) was used.
- Sysmocom USIM with known credentials inserted into the UE. The one used in our setup was a sysmoISIM-SJA2.
It is recommended to keep the UE with the airplane mode turned on until the NGC and RAN have been successfully deployed and connected.
Additional Requirement: ettus-device-plugin Daemonset
You need another prerequisite in your Kubernetes cluster in order to complete this deployment successfully. You will have to deploy an ettus-device-plugin Daemonset that is meant to manage the USRPs as Kubernetes Node Resources and automatically mount them in the corresponding Pods.
Go to https://github.com/Gradiant/ettus-device-plugin, where you will find additional information and where the corresponding Kubernetes manifest is located (ettus-daemonset.yaml). Then, execute the following command in order to create the corresponding Kubernetes resource:
kubectl apply -f https://gradiant.github.io/5g-charts/docs/open5gs-oaignb/ettus-daemonset.yaml
After this is completed, you can rely on Kubernetes to place the device plugin’s Pod onto Nodes, to restart the daemon Pod after failure, and to help automate upgrades.
Deployment NGC and registration of subscriber
First, deploy the NGC (open5gs) using the 5gSA-values.yaml file provided in order to overwrite some of the default values of the Open5GS chart:
helm install open5gs oci://registry-1.docker.io/gradiant/open5gs --version 2.0.8 --values https://gradiant.github.io/5g-charts/docs/open5gs-oaignb/5gSA-values.yaml
These new values will:
- Disable the Open5gs EPC, deploying only the functions of the Open5gs 5G SA Core.
- Set the MCC, MNC, TAC to be used by the AMF, as well as the SST and SD for the slice, which are also used by the NSSF. Notice that these values match the ones mentioned later for the subscriber’s registration, being also tied together with the sysmocom USIM’s credentials.
- Disable the Ingress for accessing the Open5GS WebUI.
- Enable the populate option, which will create a Deployment using the
gradiant/open5gs-dbctlimage. This will provide an easy way to manage the subscribers. In addition, the initCommands specified will manage the registration of the corresponding subscriber. As you can see, the subscriber is registered by providing the imsi, key, opc, apn, sst and sd, thus configuring already its corresponding slice. Take into account that the values provided are tied together with the sysmocom USIM’s credentials in the UE.
The successful registration can be verified following 2 different approaches:
- Directly through MongoDB
kubectl exec deployment/open5gs-mongodb -ti -- bash
mongo
use open5gs
db.subscribers.find().pretty()
- Using the Open5GS WebUI: forward a local port to a port on the corresponding Pod by specifying the WebUI Service. Then, the Open5GS WebUI will be available at
localhost:3000. To do this, execute:kubectl port-forward svc/open5gs-webui 3000:3000
Deployment RAN
Before installing the corresponding helm chart, make sure of having properly connected your USRP to one of your cluster’s nodes.
Now, deploy the RAN (oai-gnb) using the gnb-values.yaml file provided in order to overwrite some of the default values of the oai-gnb chart:
helm install oai-gnb oci://registry-1.docker.io/gradiant/oai-gnb --version 0.3.1 --values https://gradiant.github.io/5g-charts/docs/open5gs-oaignb/gnb-values.yaml
Thus, this deployment will launch the eNodeB and connect it to the Open5GS NGC.
It is important to notice that the default values in th gnb section for mcc, mnc, mncLength, tac, sst and sd0 match those configured in the open5gs chart and the registered UE.
In addition, take into account that the value given for gnb.amf must match the name of the corresponding AMF service deployed by the open5gs chart. Therefore, in case you use a differente release name for the open5gs chart, make sure that this value is set accordingly.
The value for image.tag provided is set to 2022.w20, since it was the version of the gradiant/oai image tested in this tutorial.
Verify EPC and RAN connectivity
Connection between SMF and UPF (C-Plane and U-Plane of NGC)
Check that the SMF gets associated with the UPF’s address:
kubectl logs deployment/open5gs-smf -f
Connection between AMF and gNodeB
Check that the AMF accepts and adds the gNodeB:
kubectl logs deployment/open5gs-amf -f

Check that gNodeB is deployed successfully and that is waiting for UE’s detection:
kubectl logs oai-gnb-0 -f
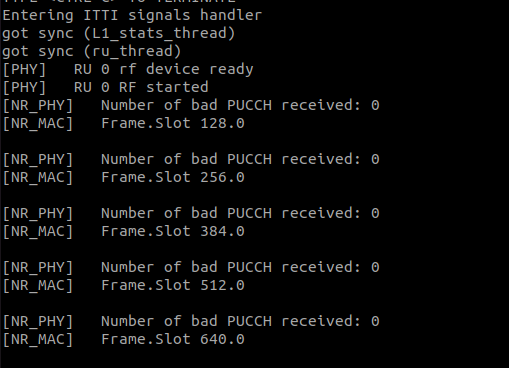
Connect UE to the network
Once the NGC and RAN are deployed and successfully connected as shown above, the UE will be able to connect to the network. Make sure that it has de sysmocom USIM with the registered credentials correctly inserted.
Also, check the APN configuration in the UE. It has to be enabled the following APN:
- APN name: internet
- APN: internet
- APN type: default
- MCC and MNC matching those previously set for the AMF and NSSF
At this point, you can turn off the airplane mode in the UE so it starts attempting to connect to the network.
Verify UE’s connectivity
Check that the UE got successfully attached to the network:
kubectl logs deployment/open5gs-amf -f

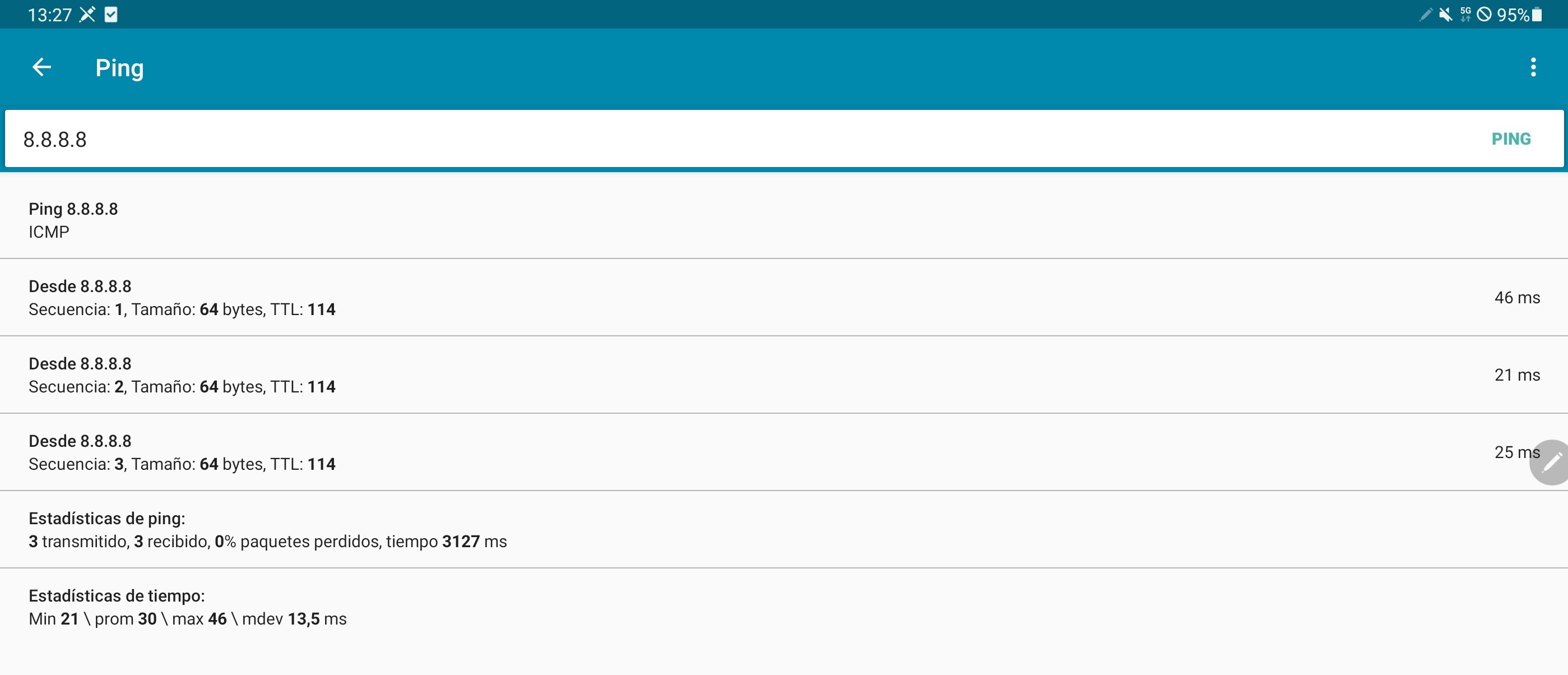
We installed and used the PingTools application in the UE in order to test the UE’s connectivity. Open this application and, through the ping section of the app, you can easily test the UE’s connectivity to the gNodeB and to the Internet:
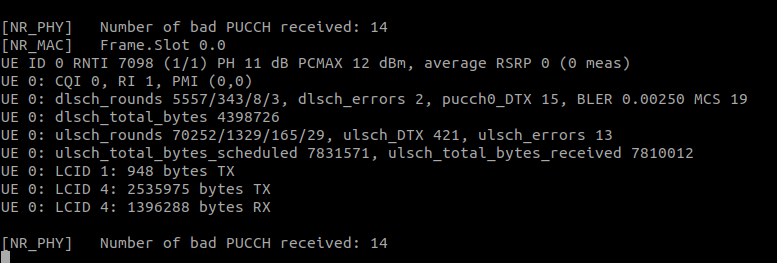
Check that the gNodeB is seeing data from the UE:
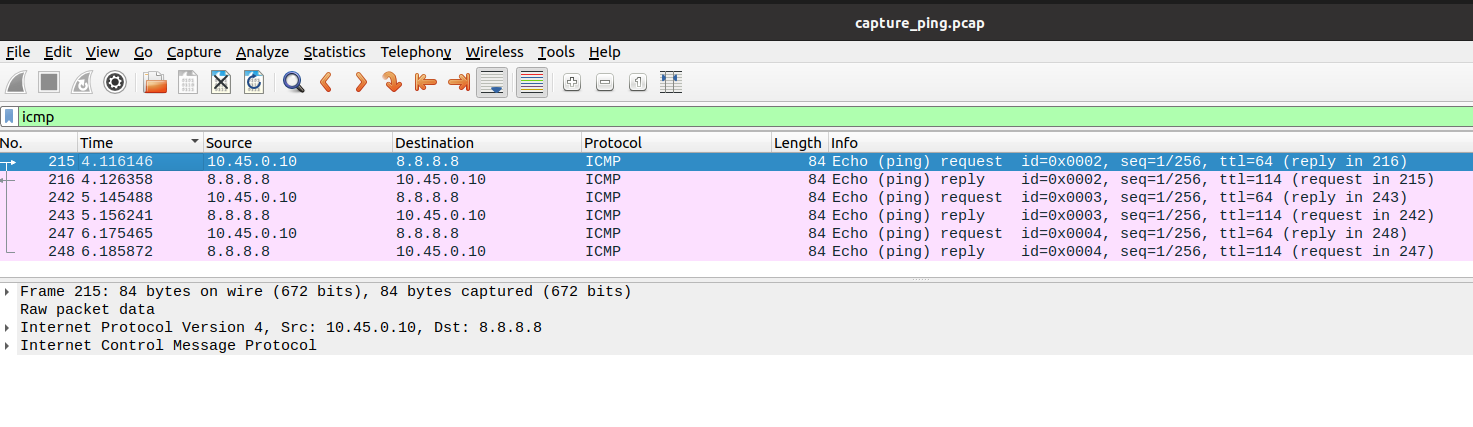
It’s even possible to check that the UEs’ traffic is being routed correctly through their PDU sessions, capturing the packets in the UPF. The installation of tcpdump in the corresponding pod is needed in order to complete this check:
kubectl exec deployment/open5gs-upf -ti -- bash
apt update && apt install tcpdump
tcpdump -i ogstun
Clean
Clean the deployment for this demo by uninstalling the 2 helm charts previously installed:
helm uninstall oai-gnb
helm uninstall open5gs